Aegon AM: Where are the opportunities in Asset Backed Securities…
Aegon AM: Where are the opportunities in Asset Backed Securities…

…that can meet ESG risk and positive impact objectives?
By Gerard Moerman, Head of Fiduciary Services & Investment Solutions, Brunno Maradei, Global Head of Responsible Investments, and Egbert Bronsema, European ABS Senior Portfolio Manager
Markets have retraced most of their losses
The drawdown in the markets provoked by Covid-19 reached its lowest level during March. Since then, the spreads of liquid asset classes have tightened and performance has recovered around 70-80% of the losses. This article is a summary of the first webinar (in a series of three) on Alternative Fixed Income and Responsible Investments. Gerard Moerman discussed with Egbert Bronsema and Brunno Maradei on where the opportunities in Asset Backed Securities are that, apart from enhancing return and diversification, can help investors manage their ESG risk objectives.
Complexity and size premium traditionally characterize Asset Backed Securities. In addition, a strong protection system found within Asset Backed Securities has supported an attractive risk/return profile –especially within the lower-rated securities. The ABS setup is also able to manage ESG risks through tailored techniques. Full details of the conversation can be heard in the webinar playback.
As yields tighten, where next for Institutional Investors?
Covid-19 led to big movements in the financial markets. Spreads reached their highest point on March 23 and, from that point onwards, they have tightened. This implies a possible turning point in the markets where a short opportunistic window to buy at elevated spreads may now have passed. However, as long as uncertainty remains in the markets, there will still exist some opportunities. Investors are now wondering what is next and what options they can take into account for their strategic asset allocation and long-term objectives.
Once again, alternatives stand out as an option to gain additional yield driven by factors such as illiquidity, size and complexity premium. In addition, alternative strategies showed a resilient performance during the previous market turmoil, bringing to their holders diversification benefits as well as stable returns compared to more traditional investments.
The financial markets have seen a growth in new opportunities within the fixed income space. This has been particularly evident with the growing trend towards alternatives from institutional investors. Another important trend in the global financial markets is the move towards ESG integration and impact investments. On top of the already known risk reduction benefits intrinsic to alternative investments e.g. diversification and low volatility, ESG risk can also be well managed in selected alternative asset class portfolios.
Furthermore, some strategies are specifically addressed to impact-related activities and are designed to be considered impact investing.
Performance per asset class
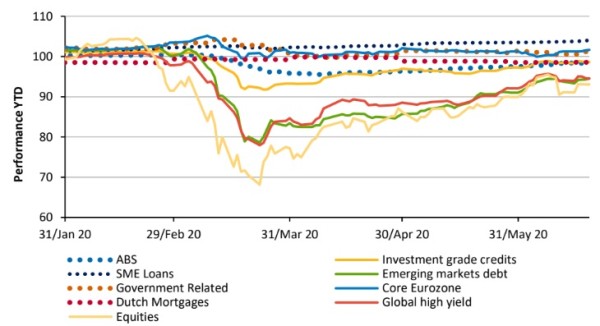
Source: Aegon Asset Management
Asset Backed Securities as a solution looking for additional yield and ESG integration
Within the alternative fixed income space, three strategies that align responsible investing stand out. The first one to be discussed is Asset Backed Securities (ABS). ABS are instruments secured by a pool of assets i.e. they are secured bonds. The pool of assets can vary in nature e.g. mortgages, credit card loans or student loans, but they all have in common that the pools backing the ABS are homogenous i.e. they are one type and never mixed. This facilitates the risk assessment process and transparency, that has actually improved after the Great Financial Crisis, is an important part of what makes ABS so unique within the fixed income space.
The individual underlying loans in the ABS can be analyzed one by one. Relevant data is more available and includes detail on coupons, borrowers income, loan size, value of asset, geographical location and many more characteristics. Based upon on detailed information at the level of the individual loans, it is possible to carry out solid research on the creditworthiness of an ABS and its probability of default. Such a level of granularity, also allows not only traditional risks (such as market, prepayment and credit risks) to be assessed, but also makes it possible for ESG risk management techniques to be fully integrated within the asset class.
ABS are part of the structured finance space which provides protection in case of defaults. Investors can participate in any part of the capital structure of the pool, from the AAA tranche to the equity tranche. Two lines of defense come into play within this structure: the first one is the excess spread, which is the amount of interest that is left after paying all the income for bonds in the ABS structure. In case of losses in this step, first losses reduce the income to the equity tranche. At this stage is when the second line of defense appears, which is the subordination: the lower rated tranches provide support for the higher rated tranches. Aegon Asset Management has not suffered any default related losses within ABS.
Moving down the ratings spectrum compensates ABS investors
The persistent hunt for additional return, especially after the elevated spreads have tightened, is leading investors to explore lower rated and higher yielding bonds. Within the high yield spectrum, ABS offers a return that is relatively attractive compared to the underlying risks, highlighting low defaults and good recovery rates as the main contributors to such a reduced risk.
Putting the aforementioned protection system in practice, it is possible to analyze how a BB-rated UK non-conforming bond behaves in times of stress. Using historical data including financial turmoil periods like the global financial crisis, the losses provoked by the defaults are avoided due to the two lines of defense existing in the ABS structure. Moreover, even if the historical data is stressed by a factor of 200% there are still no losses realized. The additional yield available from such a BB-rated non-conforming bond is currently 525 basis points over Euribor. This implies a material yield pick-up of 1.5% above a traditional high yield corporate bond of similar characteristics.
The combination of the protection system and premium found in not only traditional investment grade ABS but also within the high yielding space has understandably created interest amongst institutional investors who have the understanding and capability of performing appropriate due diligence on the asset class.
ESG can be fully integrated within the ABS space
ESG factor analysis is an important part of our research approach for ABS. Origination and securitization risks are critical governance risks that require considerable efforts to analyze. The goal is to identify the originator’s ESG practices, aiming to avoid poor practices such as predatory lending, in order to reduce regulatory and reputational risks. The securitization risk analysis on the other hand seeks clear and transparent processes, avoiding common risk-sharing traps.
Going deeper, material ESG risks associated with the pools of collateral are analyzed, where they can have an impact on the credit characteristics of the asset pools. Environmental and social factors can translate into defaults for instance. The collateral ESG risks are very case-specific and hence need to be assessed on a case-by-case basis. Some of the material risks that can affect ABS include structural changes in the economy and society that can in turn influence the value and the risk profile of the assets. Material ESG risks for a commercial mortgage backed security will for example be quite different to those facing a car loan ABS.
Country specific ESG risks are also taken into account but with a relatively lower weight. The idea is to assess the ESG risk profile of a country and use it as a proxy for the ESG characteristics for the collateral pool. Environmental protection regulations within a country, for instance, can translate into less environmental risk for a pool of collateral originated in the country.
As opposed to the traditional investments universe e.g. equities and corporate bonds where ESG integration is very wide- spread and availability of data disclosure and research tools is advanced, less work has been done for other asset classes, particularly within the structure credit and securitization universe. This is acknowledged to be a challenge for investors aiming to systematically integrate ESG risk analysis, but it is also an opportunity. The tailored ESG data collection and analysis we conduct adds material value and makes our approach relatively unique in the ABS investment space.
Lastly, engagement with issuers is a vital aspect in order to get a holistic view of the originators, their assets and the collateral. Data availability, for instance, leads us to conclude that, despite an increased amount of information available at loan level, ESG integration is still in its infancy for this asset class and, thus, engaging with issuers is fundamental in reaching the expected level of granularity and delivering high quality ESG risk analysis and integration.
Opportunities in ABS and high yielding ABS are not opportunistic
A first observation is that, historically, ABS have offered a premium over corporate bonds’ spreads. At the lowest rating tranche of BBB investment grade ABS, between December 2012 and April 2020, this premium was in average 85 basis points. Moreover, if we analyze the CLOs space, an even larger premium is constantly seen ─216 basis points in average. Thus, the amount of premium offered by ABS depends on how much risk and what kind of exposure the investor is willing to take.
Secondly, next to a proper fundamental analysis, looking at the ABS capital structure it is observed that the risk return offered within the lower rated tranches is more attractive. Recent research done by AAM has shown that high yield bonds give a larger risk adjusted return than other asset classes after a financial turmoil. Whether this is expected to apply for ABS securities or not, requires a structural analysis of the asset class and its market.
The number of participants in the ABS market is not expected to change significantly, thus potentially preserving the premium observed. As mentioned, ABS as an asset class, is preferred by some institutional investors with a good understanding and skill to perform thorough due diligence. ABS has a punitive capital treatment under regulation for
European insurers and retail, wholesale and relatively small institutional investors, are not foreseen to enter into this market.
Thus, given the structural consistency of the ABS market –mostly considered by total return investors, the long-term premium of ABS and the better risk-adjusted return of the high-yielding spectrum, are not expected to change.
Conclusion
Alternative fixed income and responsible investment strategies are gaining weight in investors Strategic Asset Allocation. ABS is an asset class where these two trends can meet. Not only do traditional investment grade ABS offer a yield pick-up over liquid corporate strategies, but also the high yield spectrum of ABS also offers an attractive risk-adjusted extra yield. Higher yielding ABS also currently have a better return-risk profile within the capital structure. Moreover, ABS is characterized by a 2-lines of defense protection system which is the main driver in reducing risk within the asset class. From a portfolio perspective, diversification is an important risk-reducing element, mostly driven by exposure to consumer risk. The historical premium achieved within the ABS market is not likely to change due to the relatively static structure and participants within the market.
ESG can be fully integrated in investment process in the ABS space. The added value of a tailored ESG integration process can not only reflect the objectives of responsible investors, but also reduce financially material ESG risks. ABS issues facing reduced ESG risks, for instance, performed better than their peers during the recent financial turmoil according to our analysis.
We hope you enjoyed this first webinar out of three in the Alternative Fixed Income and R.I. series. If you have any follow-up questions regarding opportunities in ABS that can meet ESG risk objectives or about how to integrate ABS in your strategic asset allocation, please get in touch with your regular Aegon Asset Management contact.










